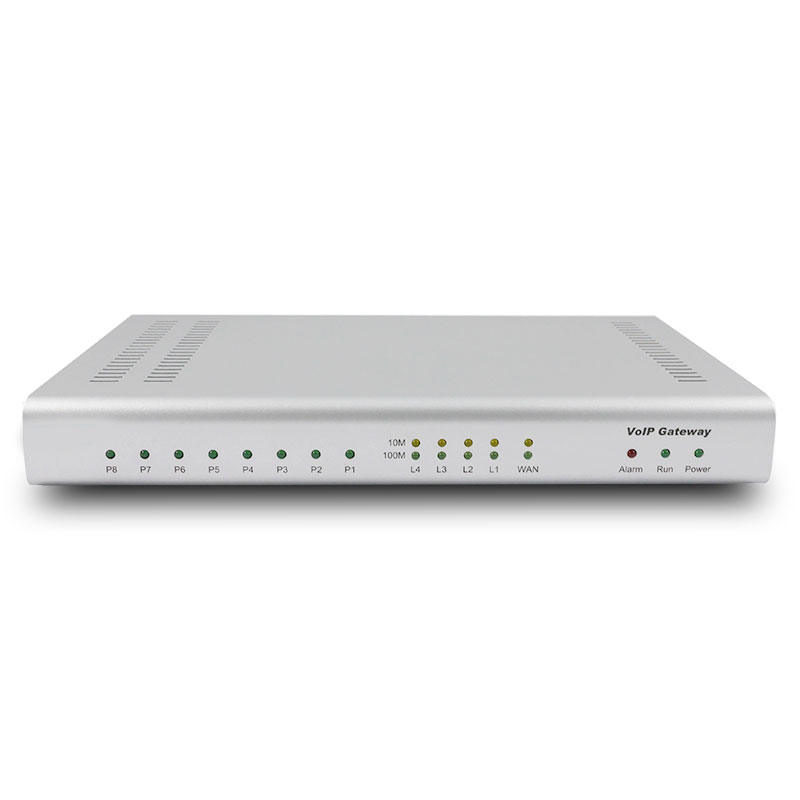
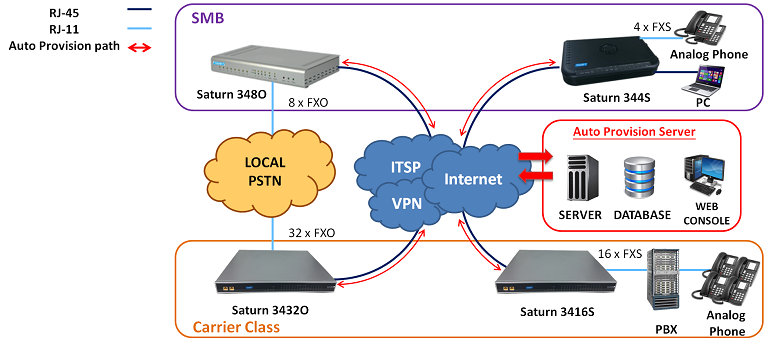
Tainet Saturn VoIP Gateway provides a connection platform between traditional POTS lines and the Internet. Over various broadband technologies including xDSL, HFC, wireless and fibre, Saturn carries toll-quality voice, fax and data traffic simultaneously in a cost-effective way. Also, the VoIP Gateway supports intelligent features like a long loop, line testing, polarity reversal, caller ID, call transfer, call waiting and 3- way calling. The ideal applications include MTU/MDU, virtual PBX, IP Centrex, PBX extension and hosted telephony services
Features
- RFC 3261 SIP protocol VoIP Gateway
- 4 / 8 FXO and 5 Ethernet ports
- 1WAN + 4LAN, RJ-45 10/100Ethernet
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
- T.30 and T.38 compliant
- Line reversal and metering tone (12K/16KHz)
- Ethernet switch function with QoS and VLAN
- IGMP Proxy/Snooping
- Advanced calling features, call parking and more
- WEB based configuration (HTTP/HTTPs)
- TR-069, TR-104, DHCP Auto Provision
- SNMP V2c/V1
- Busy Tone cadence auto learning/detection
Specifications
Voice Feature
- G.711 a /μ-law, G.723.1, G.726, G.729A
- Silence Suppression & Detection
- Comfort Noise Generation (CNG)
- Voice Activity Detection (VAD)
- Echo Cancellation (G.165/G.168)
- Adaptive (Dynamic) Jitter Buffer
- Programmable Gain Control
- Multiple SIP Proxy server entries with failover mechanism
SIP Method Support
- ACK, BYE, CANCEL, INFO, INVITE, MESSAGE, NOTIFY, OPTIONS, PING, PRACK, PUBLISH, REFER, REGISTER, SUBSCRIBE, UPDATE
SIP Call Features
- Peer to Peer Call
- Call Hold / Retrieve
- Call Waiting
- Call Pick Up
- Call Park / Retrieve (with SIP Server)
- Call Forward – unconditional, busy, no answer
- Call Transfer – attended, unattended
- Speed Dialing
- Repeat Dialing
- Three-way Calling
- MWI (RFC-3842)
- Hot Line and Warm Line
SIP Call Management
- Support Outbound Proxy
- Support up to three SIP servers
- SIP Registration Automatic Failover
- Group Hunting
- Privacy Mechanism /Private Extension to SIP
- Session Timers(Update / Re-invite)
- DNS SRV Support
- Call Types: Voice/ Modem/ FAX
- Call Routing by Prefix Number
- User Programmable Dial Plan
- By routing Calling Number Manipulation
- RADIUS CDR Client
- Manual Peer Table(for P2P calls)
- E.164 Numbering, ENUM support
SIP Account Management
- By port registration
- By device registration (share account)
- Mixed mode (Hunt number for inbound, by port number for outbound)
- Invite with Challenge
- Register by SIP Server IP Address or Domain Name
- Support RFC3986 SIP URI format
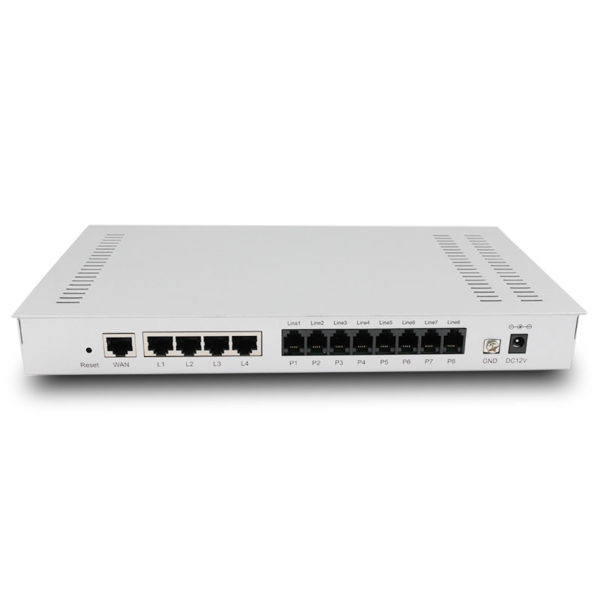
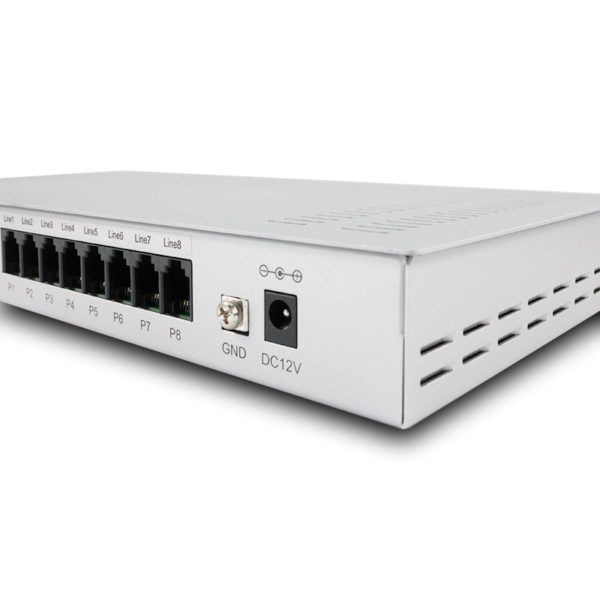
Physical Interface
- WAN: 1 x 10/100/100M Ethernet, auto crossover, auto speed negotiation, RJ-45
- LAN: 4 x 10/100/100M Ethernet, auto cross-over, auto speed negotiation, RJ-45
- RJ-11 telephone connectors
- Power jack, Power switch
- Reset button
Telephony Specification
- In-Band DTMF, Out-of-Band DTMF Relay (RFC2833 or SIP INFO)
- DTMF / PULSE Dial Support
- Caller ID Detection(FXO):
.DTMF
.FSK-Bellcore Type 1 & 2
.FSK-ETSI Type 1 & 2
.FSK-NTT
.FSK: Calling Name, Number, Date and Time, VMWI
- FXS metering pulse:
.Polarity Reversal
.12kHZ calling tone
.16kHZ calling tone
- Polarity Reverse
- T.30 FAX bypass, T.38 Real-Time FAX Relay
- Fax and Modem over IP (up to 14,400bps)
- ROH Tone( Receiver Off-Hook Tone@480 Hz)
- Loop Current Suppression
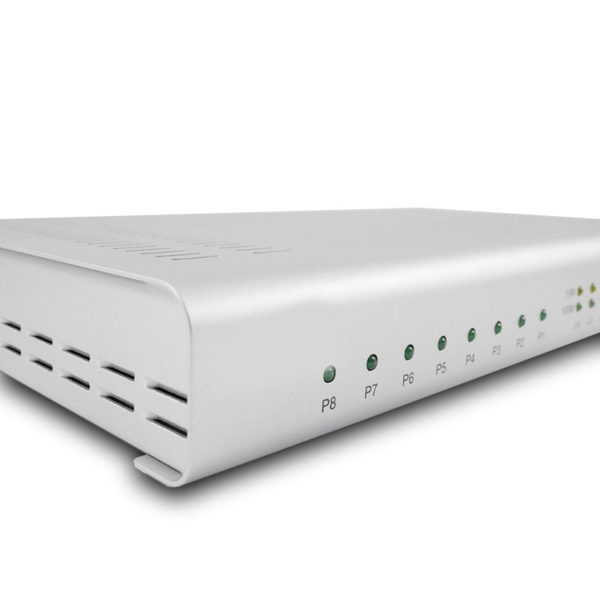
LED Indicators
- Saturn 344O: Power, Provision/Alarm, Register, WAN, LAN1~4, Phone1~4 (or LINE1~4 for FXO)
- Saturn 344O: Power, Provision/Alarm, Register, WAN, LAN1~4, Phone1~8 (or LINE1~8 for FXO)
Accessories
- RJ11 cables
- RJ45 cables
- Power adaptor
- User Manual in CD
General Information
- Dimensions :
Saturn 344O: 202 (W) x 172 (D) x H 35 (H) mm
Saturn 348O: 302 (W) x 179 (D) x H 45 (H) mm
- Weight :
Saturn 344O: 430g
Saturn 348O: 1.2kg
- Power: AC 100~240 V 50/60Hz input, DC 12V/1.5~2A output
- Operating temperature :0°C~ 45 °C
- Storage temperature: – 25°C~ 75 °C
- Operating Humidity: Up to 90% RH, non-condensing
NETWORK FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT
IP Network Specification
- WAN: Static IP, PPPoE, DHCP, PPTP
- Network Protocol Support:
IP, TCP, UDP, TFTP, FTP, RTP, RTCP, XR, ARP, RARP, ICMP, NTP, SNTP,
HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, DNS SRV, Telnet, DHCP Server, DHCP Client, SNTU Client,
UPnP, IGMP, IGMP snooping, IGMP proxy, RTSP ALG, SIP ALG
- NAT Functions
.Support up to 255 clients
.Port Forwarding (Virtual Servers)
.DMZ
.Port Triggering
- IPv4
- QoS Support:
.WAN: DiffServ, IP Precedence
Priority Queue
Rate Control
802.1Q (VLAN Tagging), 802.1P (Priority Tag)
.LAN: Rate Limit
- DDNS Support
.Dyndns.org (Dynamic and Custom)
Network Security Specifications
- PPTP Client
- DIGEST Authentication
- MD5 Encryption
- DoS Protection
Management
- Web Based Configuration
- Auto- provisioning (HTTP/ HTTPS/ TFTP)
- Telnet
- IVR
- FTP/ TFTP/ HTTP Software Upgrade
- Configuration Backup and Restore
- Reset to Default Button
- TR-069, TR104 (optical)
- SNMP V2c /V1
STANDARD COMPLIANCE
SIP, Voice and FAX Related Standard
- RFC1889 RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications.
- RFC2543 SIP: Session Initiation Protocol
- RFC2833 RTP Payload for DTMF Digits, Telephony Tones and Telephony Signals
- RFC2880 Internet Fax T.30 Feature Mapping
- RFC2976 The SIP INFO Method
- RFC3261 SIP: Session Initiation Protocol
- RFC3262 Reliability of Provisional Responses in Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
- RFC3263 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): Locating SIP Servers
- RFC3264 An Offer/Answer Model with Session Description Protocol (SDP)
- RFC3265 Session Initiation Protocol(SIP)-Specific Event Notification
- RFC3311 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) UPDATE Method
- RFC3323 A Privacy Mechanism for the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
- RFC3325 Private Extensions to the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for Asserted Identity within Trusted Networks
- RFC3362 Real-time Facsimile (T.38) – image/t38 MIME Sub-type Registration
- RFC3515 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Refer Method
- RFC3550 RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications. July 2003
- RFC3665 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Basic Call Flow Examples
- RFC3824 Using E.164 numbers with the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
- RFC3841 Caller Preferences for the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
- RFC3842 A Message Summary and Message Waiting Indication Event Package for the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
- RFC3891 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) “Replaces” Header
- RFC3892 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Referred-By Mechanism
- RFC3960 Early Media and Ringing Tone Generation in the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
- RFC3986 Uniform Resource Identifier (URI): Generic Syntax
- RFC4028 Session Timers in the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
- Draft-IETF-sipping-service-examples-08 for call features
Network Related Standard
- RFC318 Telnet Protocols
- RFC791 Internet Protocol
- RFC792 Internet Control Message Protocol
- RFC793 Transmission Control Protocol
- RFC768 User Datagram Protocol
- RFC826 Ethernet Address Resolution Protocol
- RFC959 File Transfer Protocol
- RFC1034 Domain Names – concepts and facilities
- RFC1035 Domain Names – implementation and specification
- RFC1058 Routing Information Protocol
- RFC1157 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- RFC1305 Network Time Protocol (NTP)
- RFC1321 The MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm
- RFC1349 Type of Service in the Internet Protocol Suite
- RFC1350 The TFTP Protocol (Revision 2)
- RFC1661 The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
- RFC1738 Uniform Resource Locators (URL)
- RFC2854 The ‘text/HTML Media Type
- RFC2131 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- RFC2136 Dynamic Updates in the Domain Name System (DNS UPDATE)
- RFC2327 SDP: Session Description Protocol
- RFC2474 Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field)
- RFC2516 A Method for Transmitting PPP Over Ethernet
- RFC2616 Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.1
- RFC2617 HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication
- RFC2637 Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
- RFC2766 Network Address Translation – Protocol Translation (NAT-PT)
- RFC2782 A DNS RR for Specifying the Location of Services (DNS UPDATE)
- RFC2818 HTTP Over TLS (HTTPS)
- RFC2916 E.164 Number and DNS
- RFC3022 Traditional IP Network Address Translator
- RFC3489 STUN – Simple Traversal of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Through Network Address Translators (NATs)
Application